概述
Atlas一个运行于Android系统上的一个容器化框架。为了实现这一目标,在编译器和运行期,Atlas都做了很多工作。本文是一个入门级别的文章,梳理从gradle配置到生成最终apk的期间,Atlas框架到底搞了哪些事情。
代码以 官方demo 为例。
gradle分析
gradle部分,我们只用看主工程app和bundle的配置就可以了。
app
build.gradle
1 | # 第一部分 |
可以很清楚的看到,gradle的配置主要分为三大块,依次是标准的android插件配置、atlas插件的配置,以及依赖管理部分。我们重点看最后两个部分。
Atlas插件配置
atlas插件有很多参数,这里只关注demo中出现的重点参数,其它设置大家可以查看官方文档。
1 | atlas { |
atlasEnabled 开启atlas插件的开关,在编译期会做很多事情
- merge各个bundle的manifest到app中
- 将bunde的资源进行分段
- 为四大组件预留一些坑位
- 生成一些class,记录bundle的关键信息
- 打包bundle等等
autoStartBundles 指定第一个需要启动的bundle,在Atlas框架初始化完毕后,会执行这里这里配置bundle的代码。
preLaunch 自定义初始化入口,这个类需要实现AtlasPreLauncher接口,回调时机是在atlas对系统进行hack之后,atlas框架开始初始化之前。
依赖管理配置
接着看依赖配置部分
1 | atlas { |
dependencies 主要分为三个部分
- comile xxx
- bundleCompile xxx
- outOfApkBundles =[‘xxx’]
compile : 常规的打包配置,会将依赖代码打入到dex中去
bundleCompile : atlas 的配置项,表示apk的bunde依赖,即apk是由这些bundle共同组成。
bundle中的代码不会打入dex中去,bundle将以libxxx.so文件的形式,放在apk的lib目录下,随包发布
outOfApkBundles : 指定远程bundle
比如在demo中,firstbundle、secondbundle、publicbundle 会打入apk中,而remotebundle不会
小结
可以看到,在atlas框架中,主app只是一个壳子,只是用来配置打包参数的
比如在demo中,配置了以下打包设置
- app的包名、版本号…
- 需要打入dex的代码 (appcompat…)
- 随包发布但是不打入dex的代码 (firstbundle、secondbundle、publicbundle)
- 独立打包,用于后续的动态下发 (remotebundle)。
盗用一张老大的图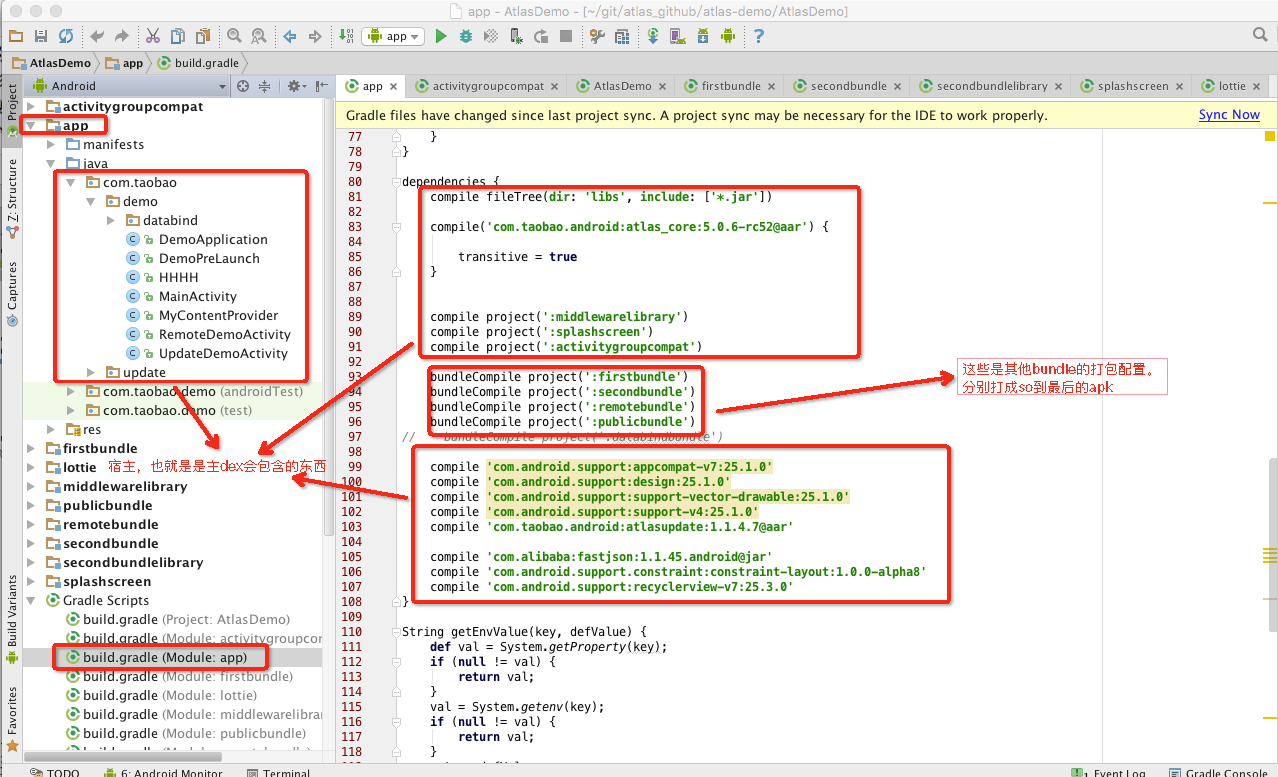
bundle
以secondbundle为例,看一下bundle中gradle的配置
1 | apply plugin: 'com.android.library' |
首先apply plugin: 'com.taobao.atlas'和awbBundle true表明启用了atlas插件,并将当前模块编译成awb形式的bundle供主apk使用。
而在 dependencies 中可以看到有两种形式的依赖
| 依赖方式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| providedCompile | 主dex中已经打入了必要的公用代码(appcompat、middlewarelibrary),在runtime时,atlas框架会自动找到主dex中的class使用,所以secondbundl就不需要在重复打入 |
| compile | secondbundlelibrary之前并没有打入主dex中,因为这只是secondbundle所需要的依赖。最终会将secondbundle和secondbundlelibrary的打在一个同一个dex中,加上两者的资源,成为一个bundle |
apk结构分析
在看完gradle的配置之后,我们反编译demo的apk,看一下最终生成的结构。
host
manifest
首先,贴一张反编译后的manifest

可以看到,manifest中的内容大概分为三大块
- host 的manifest部分
- bunde 的的manifet部分
- 额外的配置
| manifest | 说明 |
|---|---|
| host | 常规编译产生的清单数据,包括app工程自身的代码和compile依赖的代码 |
| bundle | bundle部分的清单数据,包括在app工程中bundleCompile的依赖代码和bundle自身compile的依赖代码 |
| 配置 | atlas插件在编译期生成的配置信息。比如在gradle中配置了 autoStartBundles = ['com.taobao.firstbundle'],编译时,会将firstbundle中application路径写入manifest。程序运行时,atlas会第一个执行firstbundle中DemoApplication中的代码 |
主dex
分析完manifest之后,我们看一看host的dex文件,看一看有没有对java代码动手脚。
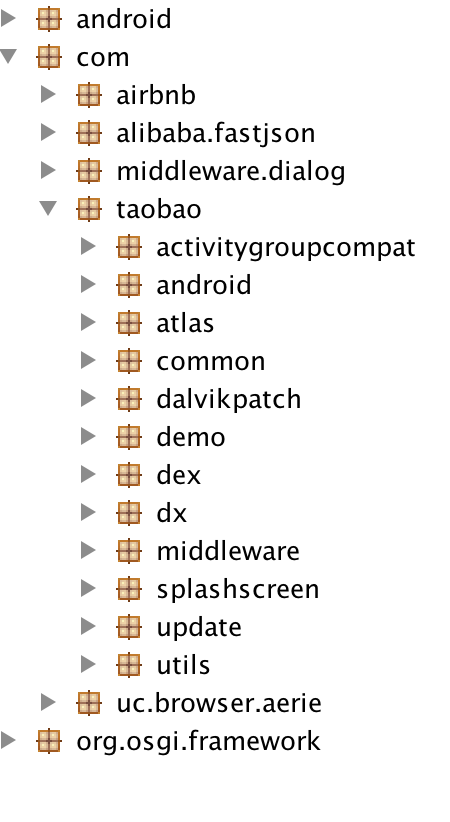
乍看之下,似乎并没有什么不妥。但是,细心的同学可能发现了,少了bundle部分的代码。
结合app工程gradle的配置,我们发现以compile开头的依赖(middleware、utils、update),都是正常将java代码打入dex中。而以budleCompile开头的依赖(firstbundle、secondbundle),他们的代码并没有在dex中。
那么,bundle的代码在哪里呢? 我们接着往下看
bundle
bundle的存放位置
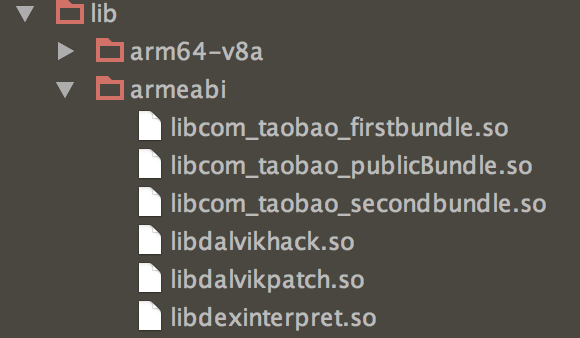
bundle的代码和资源其实独立打成了一个apk,放在了apk的lib目录下,在运行时进行动态加载。
manifest
bundle中的manifest中没有任何东西, 感兴趣的同学可以自行验证。
这部分内容在编译期已经写到app的manifest中了,这也是 组件化和插件化 的区别之一
dex
最后确认一下以secondbundle的代码,

果然,每个bundle的代码都是各自打包的。
总结
atlas将一个apk分为host和bundle两大部分
- host为共用代码资源和各个bundle的manifest信息
- bundle独立打包,拥有独立的dex和资源
- 像搭积木一样,host和不同的bundle组合编译成一个apk
参考